Are download and upload speeds really that important for online gaming? A lot of people tend to think a they are. When someone gets a hard time on a PlayStation or Xbox message thread about lagging in an online gaming session, they usually respond by telling you how good their internet package is so what’s the problem?
“How can I be lagging I’ve got Verizon 200 Mbps download and 20 upload, my internet is fine!” or something similar is usually what comes back when someone gets told they are lagging.
While the reply is no doubt true most times, it is not the most relevant thing when it comes to online gaming.
Latency, sometimes referred to as lag or “ping”, is actually far more important for online gaming and is a separate factor from download and upload speeds. Contrary to popular opinion, just having a “fast” internet package with high download and upload speeds does not automatically guarantee that gamers will be lag free online.
Other factors come into play, which we will go into in this article.
How are Download and Upload Speeds Determined?
Download and upload speeds only determine the maximum potential amount of data a router, and therefore any device connected to it, can download and upload per second. They maximum potential speeds you can get are determined by the package you have from your Internet Service Provider (ISP) and as with most things you get what you pay for.
Basic broadband packages will usually give you a maximum download speed around 10-20 megabits per second, with more expensive packages available that can give you maximum download speeds of 50, 80, 100, or even 200 or more megabytes per second.
Fibre to the Home (FTTH) packages are also available that can give up to 1 Gigabit per second download and upload speeds.
Broadband packages are advertised as providing “up to” a certain maximum download speed and in reality you will rarely, if ever, be actually able to get this maximum speed. The download speed you get at any one point in time depends on a number of factors but will mainly vary with the time of day and the number of people using the internet, both in the house and in the country in general at that time.
Download and upload speeds are actually not that important for online gaming; contrary to popular belief online gaming tends not to use that much data compared to video streaming and even a basic broadband package will provide more than enough bandwidth for gaming.
Of course if you are are downloading full games, DLC, patches and updates then higher download speeds and allowances are helpful, but for actual online gaming it is latency or “ping” that is a more important factor.
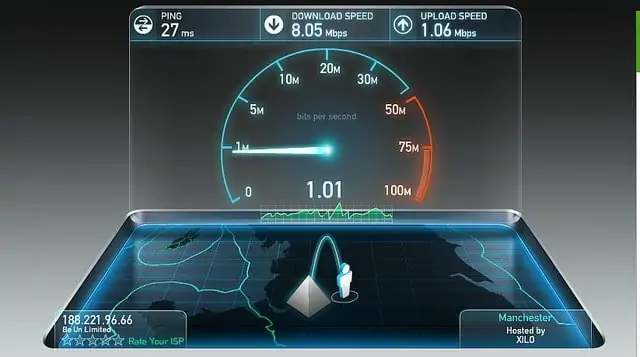
Download and Upload speeds can be useful for downloading games, but for the actual process of gaming online, having a low ping or latency is much more important
What is the Difference Between Latency (Ping) and Bandwidth (Download/Upload Speeds)?
Latency, or lag, is actually different, and is far more important for online gamers. It is the time taken for a packet of data to be sent from your console to the relevant server or other console, usually measured in milliseconds.
To use the analogy of a pipeline carrying water, bandwidth would be how MUCH water it could carry from A to B, whereas latency would be how FAST it can carry the water from A to B.
Metaphorically, increasing the thickness of the pipe would be increasing the “bandwidth” of the pipe; how much water it could potentially transport. It would not however, affect how fast the pipe could transport the water. This is the difference between bandwidth and latency, and is not well understood as people talk colloquially about how “fast” their internet is.
In a sense they are right, but not in the sense that is most relevant to latency in online gaming. Contrary to popular opinion, increasing your internet package will only influence how much data you can download per second; it will not improve latency unless your console’s connection to the router is more solid.
The “how much” part is of more concern to those downloading movies or other large files. Beyond a bare minimum of say 10 mb per second, this is of less concern to gamers (a higher download speed package will help for those gamers who download their games though, and is also recommended in houses where you have several people using the internet for high bandwidth stuff like downloading and video streaming).
The main concern for gamers is how make your console’s connection to the router as solid and reliable as possible, which is a separate issue from the maximum potential download and upload speeds you can get from your router.
To look at the issue another way, when we are talking about download and uploads speeds of our internet package, we are partly talking about how much data can be transferred to and from our router from the outside world, the “world wide web”.
But that is only part of the story as the data has to get to and from the router from the games console, and it is this delay that is the cause of much of the lag in online gaming, especially when using Wi-Fi.
Wi-Fi signals unavoidably degrade in strength the further they travel from the router, as all radio waves do from their source. In addition the more barriers a wireless signal has to travel through, before it gets to a games console, like walls, doors, ceilings, furniture etc, the more chance of the signal being further disrupted and the higher the latency will be.
In addition Wi-Fi networks have a fundamental disadvantage over wired networks in that they operate on a half duplex system, which means that devices can only send or receive data at any one time but not both simultaneously. Wired networks on the other hand operate on full duplex, meaning all devices can send or receive data simultaneously with not problems.
If the lag or “ping” is too high then gameplay will be disrupted and disjointed for one or more players; they will disappear then reappear or jump around on screen and make proper gameplay difficult for competitors.
The amount of lag that can be tolerated before online gameplay is disrupted varies greatly depending on the type of game, with slow paced strategy and turn-based games able to tolerate a higher ping whilst fast paced First Person Shooters and Racing games require a very low ping to be playable.
How Can We Influence Latency or Ping?
Ping is determined by a number of factors, some of which are are outside of our control as gamers, such as network and server problems with our ISP and the distance the data packet has to travel to the other device or server.
The geographical distance aspect is particularly important for PS4 gamers as most PS4 games work on peer to peer connections for online play, meaning that the consoles are connecting to each other rather than going through a dedicated server.
Which means that the closer PS4 gamers can be to each other geographically when playing online the better. Some games help out with this by offering matchmaking by region so you can play against players reasonably close to you geographically, preferably within the same country.
Some factors however are within our control, the main factor being the strength and quality of connection our console has to our router, before the data is then sent to the outside world.
That is something that definitely is controllable, with many gamers using Wi-Fi and suffering from lag, not knowing that there are solutions available that can help them solve this problem even if they are a long way from the router and can’t run an ethernet cable directly.
Home Networking Solutions to Reduce Ping For Gamers
For gamers still on Wi-Fi and suffering from ping, the first thing to do is get off wireless and onto wired connections instead, which are always more reliable for gaming. Obviously wired ethernet is the best option here, but what about people who can’t do this?
This is where the range of Powerline Adapters we promote on this site can come in handy, as they are designed to do precisely this – provide a strong and reliable connection between a device and the router without the need to run long ethernet cables through the house.
They use the electrical wiring of the house to transfer data, between two connected adapter plugs, from the games console to the router, providing a far more solid and reliable connection than Wi-Fi
They can be a clever solution to the problem of lag and can allow gamers to enjoy smooth latency free online gaming no matter where they are in their house.
See the quick video below for a good demonstration of how powerline adapters work. I have often found powerline adapters to give almost as good a ping as when plugged in directly with ethernet.
Click here to view the TP Link Nano Powerline Adapter, plus more models, on our powerline page.
Router Settings Which Can Reduce Ping For Gamers
Given that even most entry level fibre optic internet packages will offer more than enough bandwidth for online gaming, we would argue the real issue for gamers is to effectively manage and prioritise this bandwidth so as to minimise any delays of traffic getting to and from their consoles.
This would be the best way to reduce lag for online gaming rather than necessarily going for a “faster” internet package in terms of pure bandwidth.
As well as getting onto a wired connection if possible, there are some other ways to reduce latency on a home network by changing some router settings to manage and prioritise traffic and devices.
Quality of Service settings and Port Forwarding are both ways to reduce delays in traffic getting to a from your console and therefore reduce latency; the links above will take you to our full articles on each method, but we will also briefly summarise them here.
1. Quality of Service (QoS) – Configuring QoS settings allows you to prioritise traffic on your router on a device level basis; in other words it is possible to use QoS to tell your router to process all traffic to your console first before any other devices in the house, reducing delays in data flow and hopefully latency as well.
Here is how you configure QoS in very brief form:
- Find the MAC address of your PS4 or other console in Connection Settings/Status
- Log into your router (type 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1 into any browser, plus the router password)
- Find QoS Settings if they are available
- Select your PS4 using the MAC address you found earlier.
- Set the priority to Highest or Maximum.
- QoS is not available on all routers.
- See our article on QoS for more information.
This is especially useful in high internet use houses where you have lots of people using the internet at the same time for different things, all demanding bandwidth simultaneously.
QoS can set an order of priority to how traffic demands are met but unfortunately is not available on all routers. Many major ISPs do not offer QoS settings on their routers, something which may change in the future.
2. Port Forwarding – This is also a great method to reduce lag for gaming consoles, as again it instructs your router to automatically forward all traffic to your games console without any filtering or delays. This again has the potential to reduce the time taken for data to get to and from your console with can reduce latency for a better online experience.
There are several ways to implement port forwarding, some easier than others and each method has it’s own benefits and drawbacks.
Some methods are more difficult and time consuming but more thorough and precise, whilst other are easy “set and forget” settings changes but offer less control and customisation.
However for games consoles we recommend using the DMZ method as the easiest, quickest way of using port forwarding.
Here are the very quick steps to use DMZ for a games console:
- Get the MAC address of your PS4 (Connection Settings/Status).
- Log into your router by typing it’s IP address in any browser (often 192.168.0.1 or .1.1) and the password.
- Find DMZ Settings under Security or Advanced or similar.
- Enter or select your PS4’s MAC address and to place it in the DMZ.
- Save settings and close.
- See our article on DMZ for more on this.
Your router will automatically forward all ports to any device that is placed in it’s DMZ zone. Whilst there are safety concerns with placing other devices such as PCs and laptops in the DMZ, it is fine to place games consoles in there as they can only download data through channels carefully controlled and secured by the console manufacturers and therefore do not have the same security vulnerabilities as other devices do.
DMZ is definitely our preferred method of port forwarding for games consoles, as it is very quick and easy to implement, can be done one a device by device basis without affecting anyone else in the house (unlike another method of UPnP) and is perfectly safe to do for games consoles at least, though we do not recommend doing this for other devices.
See our main article on port forwarding for a full breakdown of all three methods – manual forwarding, UPnP, and DMZ.
