This can be a really irritating problem for Wi-Fi users, when you get a weak wireless signal even when you are right next to your router, where you should usually have full bars and close to the maximum bandwidth. What options are available to try and solve this problem?
One of the more common reasons for this to happen is that the Wi-Fi antenna in laptops especially can be under-performing because they are misplaced or have been knocked out of place. Adjusting them can sometimes restore a strong Wi-Fi signal, and there are some other things you can test for as well to try and get a better signal.
Here are some common quick solutions to try for a weak signal near the router:
- Reset your router and device.
- Check the drivers in your device are up to date
- Check the router is upgraded to the latest firmware
- Check if other devices can connect to the router itself.
- If other devices can’t connect, the router may be faulty
- Try connecting to the other band if on dual band Wi-Fi
- Try changing the channel on the router.
- Adjust or replace the Wi-Fi antenna/card in your device.
There are also other solutions, like moving to a wired ethernet connection, either directly or through a powerline adapter to avoid Wi-Fi altogether. Failing that, then you may need to take your laptop to a local store to get it’s hardware looked at and possibly replaced or upgraded.
Let’s look at some different solutions in more detail below.
Initial Troubleshooting
Before taking your device apart (not recommended unless you are qualified) or spending any money on home networking solutions or to get your device repaired or upgraded, it is important to do some basic diagnostics with your device and router to identify what exactly the problem is.
Here are some basics things to test:
- Try using the Wi-Fi right next to the router with a couple of devices. Are you just getting this problem with one specific device, or all devices? If the former, then the device is the problem; if the latter then your router is the problem – contact your ISP for a repair or replacement.
- Try simply resetting your router and device to see if it is a one off isolated problem.
- Try also a full power cycle, where both router and device are powered off, fully unplugged from the wall for a few minutes, then powered back on. Try also a full factory reset on your router if possible – there is usually a button somewhere on the router you can press in with a safety pin or something else to do a full reset.
- Try your device on a wired connection if available. Does it work OK? If so then the Wi-Fi within the device is the problem.
- Make sure you have a direct line of sight between your router and device when testing Wi-Fi, with no obstacles at all in the way. In fairness with modern Wi-Fi this shouldn’t make a difference if you are in the same room, but worth trying.
- Once you have narrowed down that it is one specific device only which is having problems, and only when on Wi-Fi, then you know that it is the Wi-Fi hardware (the wireless antennas/cards within the device) that is the problem, and you can go about fixing it.
Adjusting the Wi-Fi Antenna On Your Laptop
Warning: any work you do on your laptop is at your own risk and you may void your warranty by opening up your laptop and attempting any repair work.
If the device you are having problems with is your laptop, then adjusting the Wi-Fi antenna can sometimes help to restore a full signal. The video above perfectly depicts the problem of having a weak Wi-Fi signal even right next to the router, and how to solve it by swapping out the Wi-Fi antenna.
What usually happens in laptops is that there are several antennas located along the sides or hinges of the laptop, which are meant to balance out the signal, pulling the Wi-Fi from whichever side is getting the best reception at that moment. However, it doesn’t always work properly if the antenna or dislodged or somehow out of place, perhaps through the laptop being knocked or dropped too much.
Counter-intuitively, the technician in the video finds that actually swapping out the AUX Wi-Fi card connection and putting it all on the MAIN connection stops the laptop doing balancing, but actually makes the signal better!
Apologies for the lengthiness of the video – he does take a while to get to the point – but the advice is sound and at the time of writing the video has a lot of positive comments saying this solution worked for a good number of people (not all though).
We do get though the not all of us are comfortable opening up laptops and fiddling around with parts. For one thing it can void the warranty of the laptop to start messing around with stuff.
You can take it to a local computer store but as the guy in the video points out, it can be expensive getting them to fix the Wi-Fi and you can find yourself with a hefty bill for something that can be done yourself in 10 minutes if you have the skill and confidence to try it.
So adjusting the Wi-Fi antenna in your laptop can be a solution which works, but it is not guaranteed to do so for everyone. It is just an option to try if you find yourself with a poor signal even right next to the router, which is a clear sign that something within the device itself is not working properly if you are not having this problem with other devices.
Using a Wired Connection Instead
Another (kind of) solution to this problem of poorly performing Wi-Fi hardware in your device is to move it onto a wired ethernet connection instead, for the best possible connection and bandwidth. If your device is right next to the router, then this is easy – just plug an ethernet cable into your router and device and you have a good connection from there.
Ethernet cables are cheaply available on Amazon.
However, if your device is normally based in a different room from the router, and you don’t want to run long ethernet cables all through the house, then a Powerline Adapter is a clever home networking solution which can allow for a wired connection to your device even at distance from the router.
Powerline Adapters consist of a pair of adapters or plugs, one of which is plugged in and connected to your router, and the other of which is plugged in and connected to your device.
The two adapters then communicate through the electrical wiring of the house to deliver a strong, wired ethernet connection between your device and router, bypassing the problems of weak Wi-Fi.
See the video just below for a demonstration of how powerline technology works.
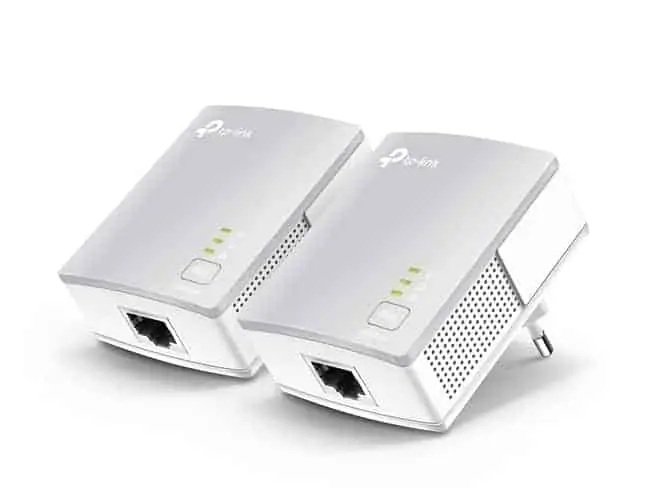

They are a great way of avoiding using Wi-Fi altogether and staying on wired connections, even if several rooms away from the router. You don’t need to run long ethernet cables through the house since the hidden electrical wiring of the house is doing most of the work.
Copper can transmit data as well as electricity and powerline technology takes advantage of this fact to bypass the need for Wi-Fi.
More advanced wireless powerline adapters are also available, which also produce a cloned Wi-Fi access point at the receiving end, but these will likely not be much use if you have identified that the Wi-Fi hardware in your device is the problem.
If it can’t connect to the main router, then it likely won’t be able to connect to a wireless powerline adapter either, so it is a case of switching to wired or getting the Wi-Fi equipment repaired.
We also get that some people just want to stay on Wi-Fi, because they find it easier and more convenient than using ethernet, especially for portability with smaller devices like tablets and notebooks.
In this case it is simply a matter of replacing the Wi-Fi antenna and card or getting it repaired, which can unfortunately cost some money. Let’s look at some other solutions which you can also try if you don’t want to be using powerline adapters or ethernet.
Some Other Solutions
Here are some other things you can try if you are struggling with a weak Wi-Fi signal even right next to the router:
- Make sure all device drivers are fully up to date where relevant. See here for updating Windows 7 drivers; see here for updating Windows 10 drivers. The network drivers tend to be the most important for Wi-Fi performance.
- If your router is dual band (ie. it has 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz access points you can connect to), then try connecting to the other band than the one you’re currently on. May deliver a better signal.
- Try changing the channel on your router into a different band. This can sometimes deliver slightly better speeds, but is only a partial solution at best and may not make a difference. See this forum discussion of a user who achieved a small increase in speeds by forcing his router into the 20MHz channel.
- Check the warranty on your device, especially if bought from a local vendor. If the Wi-Fi in the device is not working properly and you have isolated it to that device only and not your router or something else, then raise the issue with the vendor or manufacturer. Under some warranties you will be entitled to repair or replacement within a certain time period.
- If you take your laptop to a local computer shop, ask them to try the trick shown in the video above if you want, rather than a more expensive total replacement option.